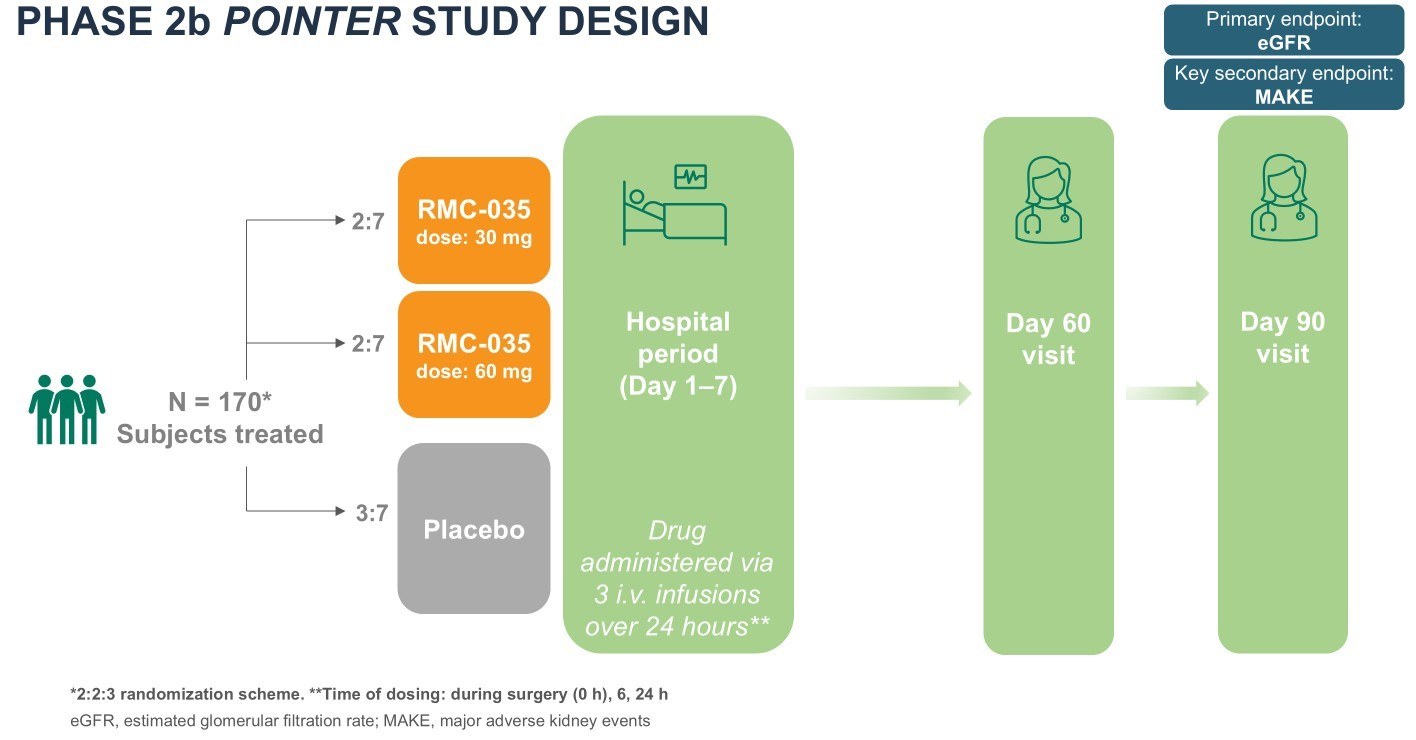
Kidney Injuries in Open-Heart Surgery
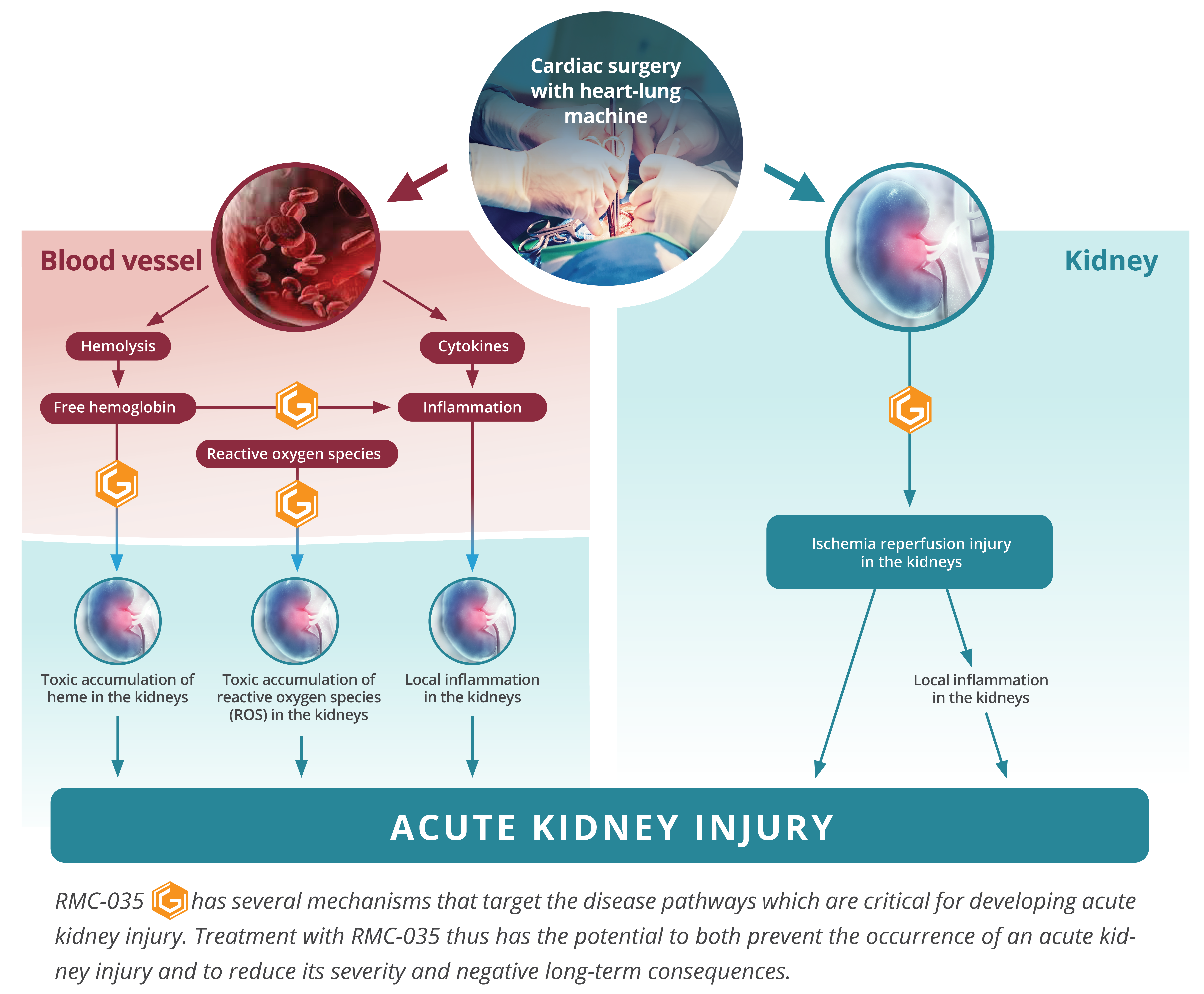
Open-heart surgery performed with the use of a heart-lung machine mainly involves coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), with or without valve or aortic root surgery (the first part of the body's main artery). This type of surgery often causes significant kidney injury.
A major reason for this is reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the kidneys (known as ischemia-reperfusion injury). Another contributing factor to kidney injury during surgery is hemolysis, where red blood cells are damaged, leading to kidney injury due to harmful breakdown products from hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying substance. Hemolysis occurs when blood circulates outside the body via the heart-lung machine and during blood transfusions, which are often administered during the procedure.
In addition to oxygen deficiency and hemolysis, secondary inflammation often arises, contributing to ongoing kidney injury, increasing the risk of scarring and permanent loss of kidney function.